MagicProspect
Open siteMarketing & Advertising
Introduction
AI-driven sales intelligence to transform your outreach and prospecting approach.
MagicProspect Product Information
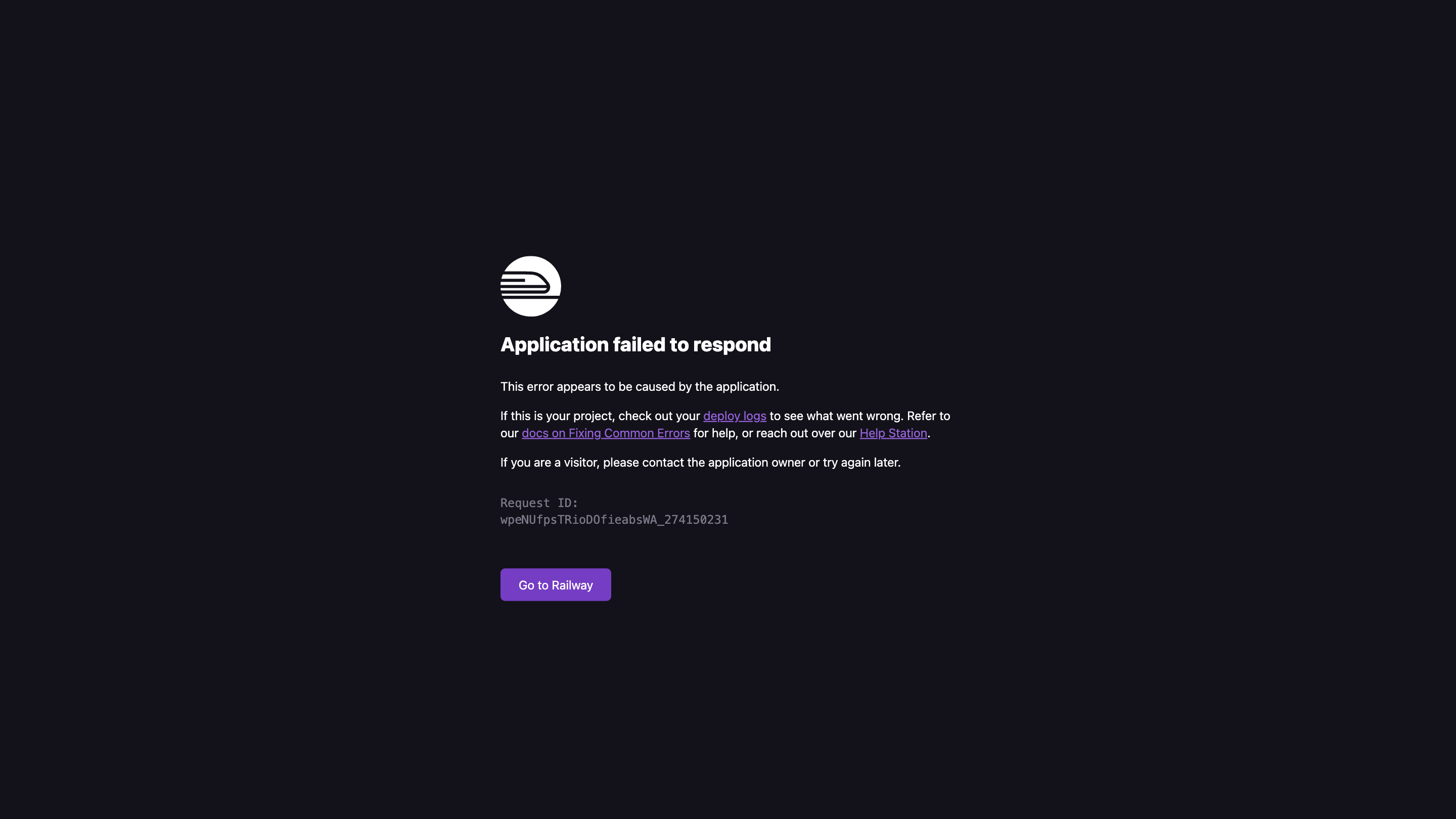
502 Bad Gateway - Application failed to respond on Railway is an error description you might see when a deployed application on Railway cannot respond to incoming requests. This guide explains what the error means, common causes, and practical steps to diagnose and recover your service. It also highlights how to monitor, retry, and stabilize deployments to minimize downtime.
What it means
- A 502 Bad Gateway indicates that Railway's frontend gateway received an invalid response from the upstream application container or service. The issue is typically on the deployed app side, the container, or the connected services the app relies on.
- It can be transient (temporary network hiccup) or persistent (misconfiguration, code crash, or resource limits).
Common causes
- The application container crashed or exited before sending a response.
- The upstream service (e.g., database, external API) is unreachable or timing out.
- Incorrect or missing environment variables, secrets, or configuration.
- Port binding or startup script issues causing the app to fail to listen on the expected port.
- Insufficient memory/CPU resources leading to OOM or throttling.
- Deployment race conditions during rolling updates.
How to diagnose
- Check deployment logs. Look for crash messages, stack traces, or startup failures.
- Verify health checks. Ensure liveness/readiness probes are correctly configured and passing.
- Inspect recent changes. Review recent commits, migrations, or config updates that could cause failures.
- Test locally. Run the app container locally to reproduce the error with the same environment variables.
- Check external dependencies. Validate database connections, API keys, and network access to external services.
- Resource limits. Confirm memory and CPU limits are adequate for the workload.
- Network policies. Ensure firewall rules or VPC settings allow required traffic.
How to fix
- Restart the service or trigger a fresh deployment to clear transient issues.
- Correct environment variables, secrets, and configuration mismatches.
- Increase resource limits if the app frequently hits memory/CPU ceilings.
- Fix code path causing the app to crash on startup or during requests.
- Ensure upstream services are reachable and implement retry/backoff logic where appropriate.
- Validate port exposure and startup commands so the app binds to the expected port.
Best practices to prevent 502s
- Implement robust health checks and proper startup probes.
- Add retry and circuit-breaker patterns for outbound calls.
- Use graceful shutdown to avoid in-flight requests during deploys.
- Monitor application and gateway metrics with alerts for elevated error rates.
- Use staged deployments and zero-downtime strategies.
When to contact support
- If the issue persists after reviewing logs, confirms no code regressions, and all dependencies are healthy.
- Provide the Request ID (e.g., G2MpHAIfSd2lj139LC-0eA_3243920489) from the Railway error page to support for faster triage.
Safety and best practices
- Do not expose internal error details in public endpoints.
- Implement proper error handling and user-friendly error responses.
- Keep secrets out of logs and use secure secret management.
Troubleshooting checklist
- Deployment logs reviewed for startup errors.
- Upstream services reachable and responsive.
- Environment variables and secrets correctly configured.
- Ports exposed and app listening on the expected port.
- Resource usage within limits; scale if necessary.
- Health checks passing and readiness probes configured.
- Recent changes reviewed for potential regressions.
What to do if you are a visitor
- Try refreshing later; transient network issues can resolve on their own.
- If you are the project owner, follow the troubleshooting steps above and review logs.
Additional resources
- Railway documentation on common deployment errors
- Logs and metrics dashboards for your project
- Help Station for community or official support
Core Features
- Clear, structured guidance for diagnosing 502 Bad Gateway errors in Railway deployments
- Step-by-step troubleshooting workflow with actionable checks
- Guidance on preventing future 502 errors through best practices and monitoring